A.I. and Robots replacing the workforce
A quick primer on GDP and declining population growth
GDP Growth Amid an Aging Population
The traditional drivers of GDP growth—population growth, productivity growth, and debt growth—are undergoing significant shifts. In recent decades, reliance on debt growth has led to borrowing against future potential, a trend that culminated in the 2008 financial crisis. Today, much of the debt growth is merely servicing existing debt, leaving little room for new investments to drive economic expansion.
Challenges with Population and Productivity Growth
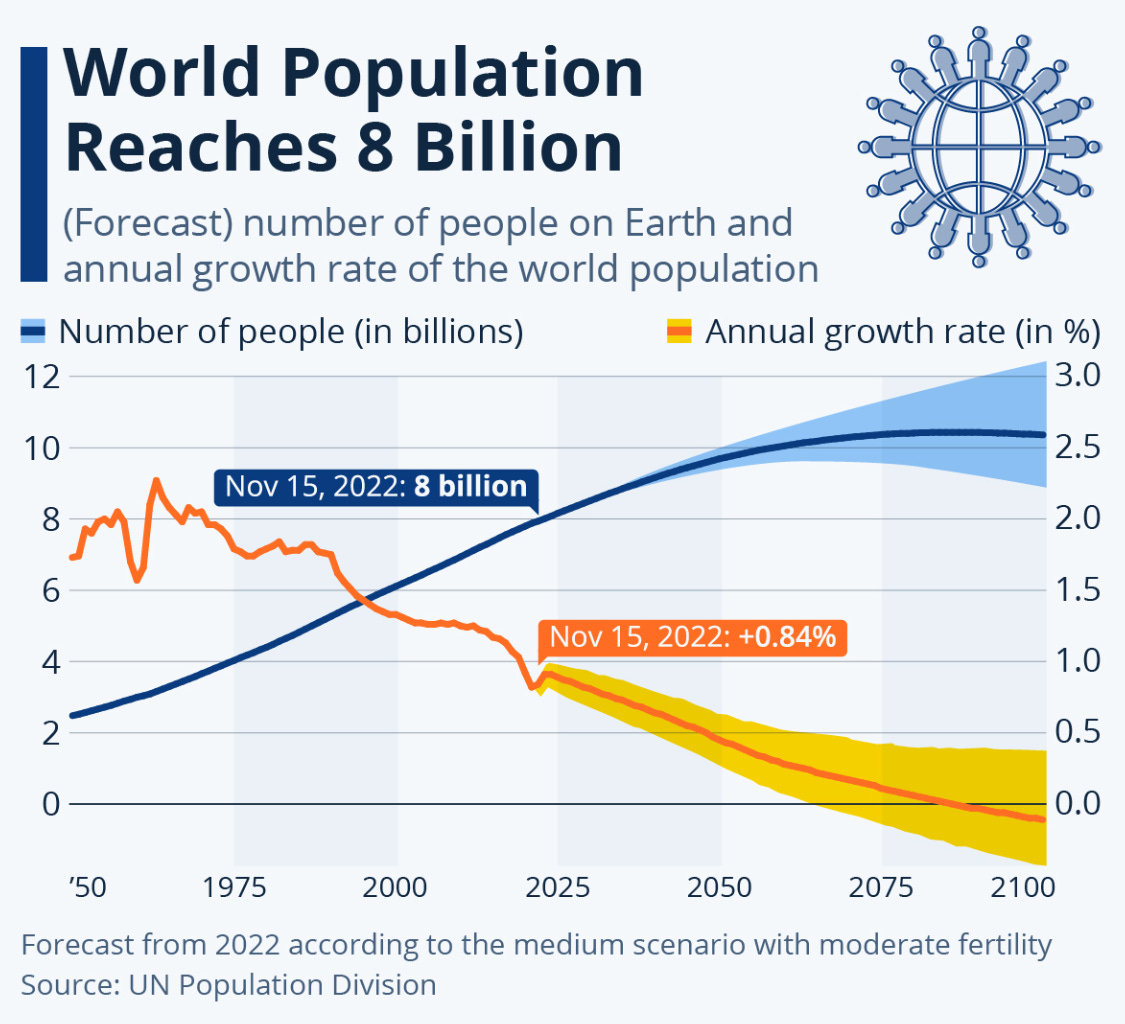
In the Western world, population growth has stagnated and, in some cases, is declining. This demographic shift, coupled with an aging population, poses a challenge to productivity growth. As the workforce ages, overall productivity tends to decline, compounding the issue. The confluence of these factors, within the broader context of the debt and debasement cycle, paints a concerning picture for traditional economic growth models.
The Role of Technology: A New Catalyst for Growth
However, technology presents a potential solution to these challenges. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and robotics is rapidly transforming industries, offering a new source of productivity and, indirectly, population growth. For instance, Amazon has expanded its use of robots from 250,000 to 750,000 in just three years, significantly boosting its operational efficiency. This trend suggests that the company's autonomous workforce could soon surpass its human workforce, as robots are often 3-10 times more productive than humans.
This shift challenges the traditional GDP formula, as AI and robotics can theoretically provide unlimited productivity growth. The question then becomes: what is required to support an infinite use of robots and AI? The answer lies in the availability of infinite electricity and computational power.
The Intersection of Technology and Green Energy
This need for vast energy resources brings the green energy narrative into focus. While some view the forced investment in Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) initiatives as unfounded or wasteful, it could play a critical role in enabling the technological future. By driving down the cost of capital for innovative energy solutions—such as nuclear, wind, solar, and geothermal energy—society can achieve significant reductions in the cost of electricity.
The potential multiplier effect of a 75% reduction in energy costs, combined with the exponential growth in productivity from an "infinite" workforce of robots and AI, is staggering. Just as the post-World War II baby boom led to a 30% increase in the population, we are on the cusp of a similar transformative period, this time driven by technological advances rather than human births.
Conclusion: Embracing the Technological Future
The future of GDP growth in an aging world hinges on embracing technology as the new engine of growth. AI and robotics, supported by advancements in energy technology, offer a path to sustained economic expansion even in the face of demographic challenges. As we move forward, the integration of these technologies will redefine the concept of productivity and growth, paving the way for a new era of economic development.
This technological future requires thoughtful planning and investment, particularly in the energy sector, to ensure that the necessary infrastructure is in place to support these advancements. As we transition to this new paradigm, it will be crucial to balance innovation with sustainability, ensuring that the benefits of technological progress are widely shared and contribute to a prosperous and equitable society.